For most men, hair loss can be pretty devastating to face.
And this is especially true if it happens in your younger years!
Your hair is an important aspect of your identity and losing it can be very overwhelming (and even depressing to some).
Studies done by the American Hair Loss Association have indicated:
- 85% of men will experience significant thinning of the hair by the time they reach 50.
- 40% of women suffer from excessive hair loss.
According to the Malaysian Society for Hair Sciences, one out of two men over 50 lose hair due to male pattern baldness. In addition, women who cross the age of 60 also experience a degree of hair loss.
Although it is common for your hairline to get wider with age, for men, it can sometimes start to happen between the ages of 17 to 28.
What is a receding hairline?
Your hairline is the edge of your hair a few centimetres above your face, where the forehead becomes the scalp. A receding hairline is when you lose your original hairline, and your hair begins to thin.
In some instances, hair can fall out from the crown portion or both.
Signs of receding hairline
Some of the notable signs of a receding hairline are:
- Visible changes in the original shape of your hairline.
- Slow or nil hair growth.
- Excessive hair loss after you brush or shampoo your hair.
- Spotting loose hair strands on your pillow/sheets/clothes, comb.
For more details, read our article on “Early warning signs of a receding hairline.”
Receding hairline stages
To put it simply, hairloss can be classified as:
- Receding hairline/ M shape appearance; or
- Crown area thinning (O shape appearance)
- Thinning all over
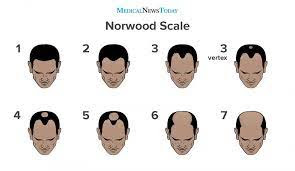
Hair loss can be classified into seven significant stages.
Stage 1- Hair loss happens at the hairline or the top of the head. It is barely noticeable.
Stage 2– Receding of the hairline starts to become more visible around the temples. This is also known as the mature or adult hairline.
Stage 3- Hair loss at the temple region becomes more noticeable.
Stage 3- Vertex hair loss occurs predominantly at the crown portion of the head, but hairline recession at the temple region remains at stage 2.
Stage 4- In this stage, there is a significant reduction in the hairline. Hair at the vertex becomes very thin and eventually disappears. The middle portion of the hair separates both areas of hair loss.
Stage 5- Receding hairline and balding at the vertex have progressed even further than in the 4th stage. In addition, hair in the middle of the scalp gets narrower, making it difficult to treat.
Stage 6- In this stage, there is extensive hair loss. Both areas of noticeable hair loss merge. The middle portion, which is used to separate the region, is not entirely bare.
Stage 7-This is the final stage where hair loss can be considered complete.
Causes of receding hairline
Many causes contribute to a receding hairline.
1. Age
This is one of the most significant factors which causes a receding hairline.
Studies done by the Journal of Investigative Dermatology revealed that up to 80% of European men have a receding hairline by the time they are 80 years old.
Once a person starts to age, hair loss will happen naturally. On the scalp, there are thousands of hair follicles growing. As each hair falls out, new follicles replace them.
When a person starts to age, the natural ability of the follicles to grow new hair diminishes. However, receding hairline in the 20s is also fairly common!.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormone factor is another common cause of hair loss. Studies have indicated that a hormone known as DHT has a direct linkage with male pattern baldness.
The hormone causes the follicles to shrink so that they can no longer produce new hair.
3. Genetic Factors
Genetics plays a vital role in receding hairlines. For example, hereditary-pattern baldness is a condition that occurs due to a specific combination of genes.
If your previous generation has premature hair loss, chances are high that you might carry the same types of genes.
4. Certain treatments or medications
Certain diseases such as high blood pressure, depression, malignancy, thyroid disorder, anaemia, and heart-related problems may lead to thinning of hair as they impact the hair growth process.
A typical example of medication with this effect is chemotherapy. This category of antineoplastic agent is used to kill rapidly growing cells (such as cancer itself) which in turn also cause a person’s hair to fall out.
5. Unhealthy Diet
A diet that is not well-balanced or does not contain essential elements like vitamins, minerals, Omega-3 fatty acids, and proteins will show up as various symptoms of malnutrition.
One of the symptoms of an unhealthy diet is receding hairline.
It is vital to ensure that your hair follicles get an ample supply of nutrient-rich blood to ensure the smooth growth of hair.
6. Smoking
Toxins present in cigarette smoke harm the hair follicles in the head by shrinking the blood vessels and thereby depriving them of proper nourishment.
Good general health means good hair growth. As simple as that.

7. Dandruff
This is a condition that causes flaky skin on the scalp. As a result, the skin falls out, leaving white flakes on your shoulders.
Unlike what most people think, dandruff doesn’t directly cause the loss of hair. However, constant itchiness due to dandruff can lead to scratching, which could damage the hair follicles.
However, if the flakes are caused by scalp fungal infection, hair loss is imminent. Treatment with medicated shampoo is definitely warranted.
Dandruff is also known to increase hair loss in people with androgenic alopecia.
8. Strong chemicals and products
Certain hair care products, shampoos, conditioners, and gels can be too strong on chemicals and may end up causing more harm than good.
You may want to stay away from hair products with bleaching agents.
How is it diagnosed?
It is advisable to see an experienced dermatologist to determine the extent and type of hair loss. Your doctor will also have your family, personal, and medical history.
He may also perform something called a “pull test”, where he will pull a few of your hair to see how many of them fall out and how easily they fall out.
The doctor might sometimes ask you to perform a blood test to determine whether you have a hormonal imbalance, thyroid problem, or other nutritional deficiency.
If necessary, they might also have to do a biopsy on your scalp tissue. For this, the doctor will remove a small tissue from the affected region, and the sample will be sent to the lab to be tested for any disease or infection.
However, you may not have to see a dermatologist immediately. A simple visit to your friendly family doctor can be a good place to start with.
Receding hairline treatment in men
Let us look at some of the effective treatment options for receding hairlines.
1. Minoxidil
This is an effective drug used for treating the scalp. Minoxidil has been approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration(FDA) to slow down the rate of hair fall.
The medication effect lasts as long as the person uses the treatment and may also provide good effects after it is stopped. However, in certain cases, baldness can return once a person stops taking the medicine.
2. Anthralin
This drug is typically used for the treatment of psoriasis. Anthralin also helps to grow new hair in some people.
3. Corticosteroids
These medications help to reduce the inflammation around the hair follicles. This will help to open them and grow new hairs. However, since corticosteroids have some adverse side effects, it is essential to discuss them with your doctor before using them.
4. Finasteride or Dutasteride
Finasteride can effectively be used for the treatment of hair loss in men. This drug helps to slow down the rate at which testosterone can be converted into DHT, thus helping in reducing hair loss.
Dutasteride, on the other hand, is a medication primarily designed to treat the prostate but can also be used to effectively restore hair growth.
Take a look at what Finasteride is and what happens if you stop taking it.
5. Laser therapy and hair transplants
Hair transplant involves taking hair from the thicker spots on the head and moving them to the front to fill the receding hairline.
Although this process is costly, it offers a long-term solution to the problem.
Another alternative is to use laser therapy, where a red light laser of 600 nm is used to induce hair growth in the affected area.
6. Essential oils
Certain essential oils such as lavender oil, rosemary oil or peppermint oil can successfully promote hair growth and health. Essential oils can be combined with carriers such as coconut oil, jojoba oil or almond oil before applying to the scalp.

7. Scalp Massage
Research has shown that regularly massaging your scalp will help to improve the blood circulation within the hair follicles. This will help the hair to grow shinier, stronger, and healthier.
8. Nutritional Changes
If you are eating a rich diet in antioxidants, it will help your hair grow strong and healthier. Antioxidants are substances that allow you to fight the oxidative stress which will age your hair.
Spinach, kidney beans, walnuts, almonds, and blueberries are all rich in natural antioxidants.
Also, read our article on “Slow your receding hairline with these 4 daily habits” and “8 proven tips for strong and healthy hair”
Conclusion
Although a receding hairline can mean the end of the world for many, it doesn’t mean that you are completely deprived of all the options.
There are numerous ways by which you could preserve your existing hair or even grow new hair. In addition, several innovative treatments are available to successfully treat male baldness.
The first thing to do is consult a family doctor or certified dermatologist to determine the exact cause of your condition and get a clear picture of the various treatment options available.
References
Emily L. Guo and Rajani Katta(7 Jan 2017)Diet and hair loss: effects of nutrient deficiency and supplement use. Available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5315033/ [Accessed 1 Aug 2021]
Hans Wolff,Tobias W Fischer,and Ulrike Blume-Peytavi(8 Dec 2016)
The Diagnosis and Treatment of Hair and Scalp Diseases. Available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4908932/ [Accessed 1 Aug 2021]
Serge Ahouansou,Philippe Le Toumelin,Béatrice Crickx, Vincent Descamps(17 June 2007)Association of androgenetic alopecia and hypertension. Available at https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17478384/ [Accessed 1 Aug 2021]
Saskia P. Hagenaars,W. David Hill,Sarah E. Harris,Stuart J. Ritchie,Gail Davies,David C. Liewald,Catharine R. Gale,David J. Porteous,Ian J. Deary,and Riccardo E. Marioni(14 feb 2017)Genetic prediction of male pattern baldness. Available at https://journals.plos.org/plosgenetics/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgen.1006594 [Accessed 1 Aug 2021]


